作为国人原创的一个大模型的基础,RWKV 还是相当优秀的。
RWKV本身的结构上最核心的是两部分Channel-Mixing 与 Time-Mixing,那么这两部分都是什么呢?
可以看一下下面的图。这个模型名字中的R, K, V 在Time-Mixing里用到了, R, K 在 Channel-Mixing里用到了。
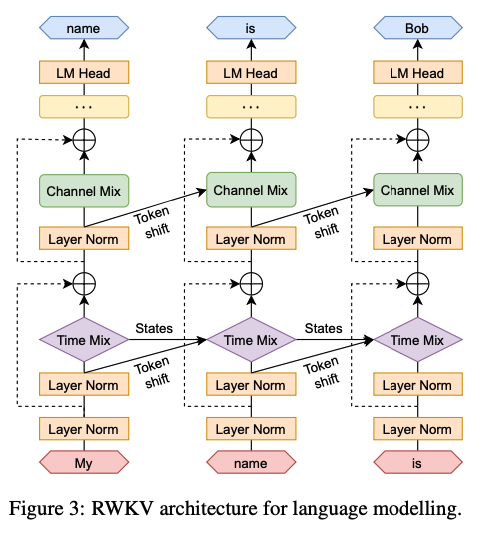
那么,R、K、V 是啥东西,它与 Transformer 中的 Q、K、V 都是同样的套路生成的吗?我们看一下官方的代码就很容易理解了。
最直接的就是用 https://github.com/BlinkDL/ChatRWKV/blob/main/RWKV_in_150_lines.py 与BlinkDL/rwkv-4-pile-430m at main 的代码与权重文件 ,直接运行调度一下,就能直接感知到了。
接下来是我的个人的理解了,方向是RNN、 Transformer、 Attention Free、 RWKV
RNN:一个足够老的神经网络架构
RNN 的提出应该有好些年了吧。以致于我引用这个都已经是 2019 年的文章了。RNN 本身在结构上是很简单的,它会引用以前的输出,把以前的 CNN 结构变成了 下面这种:
O=(X∗Wxh)∗Who 换成了 Ot=f(Xt,Ot−1) ,这样就能保留前一个状态,对于一个序列化的数据来讲这样去做 Pattern 相关的处理还是很容易的。而用 CNN 则要全部的都在感受野内才成的。。
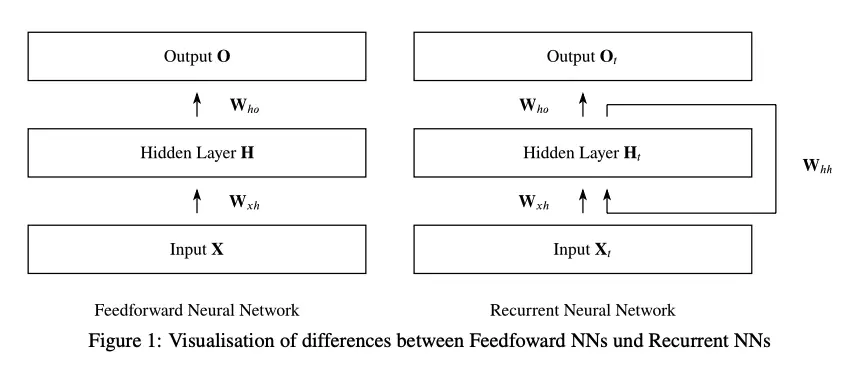
Transformer:新时代的基石吗?
无论你是否接受,AttentionIsAllYouNeed,确实是在改变世界的。最早的 Bert、GPT3、ChatGPT、GPT4 这一系列的组合下来,已经达到了整个世界的人工智能的最高峰了。从形式上看它确实比 CNN、RNN 复杂了一些,但是它的形态决定了它可以做大规模的并行连接,大模型的堆叠,并行训练。唯一的问题就是它的 Attention 机制有点儿复杂了。人脑大概率不是这种复杂的结构吧。
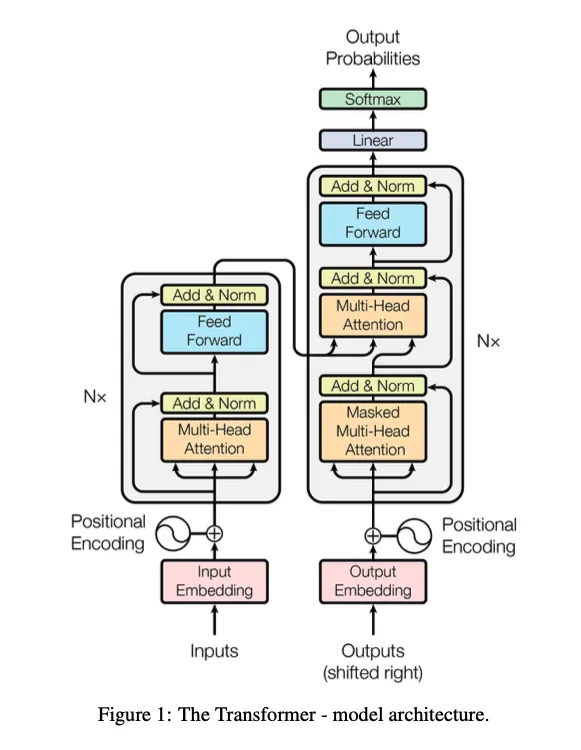
Attention Free Transformer
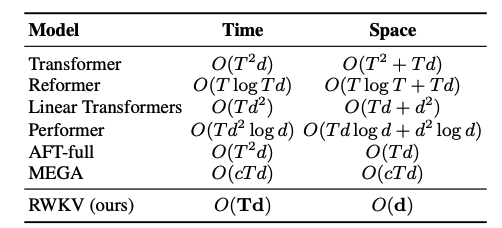
这个就是专门对 Transformer 的改进,把 Attention 改了。于是就有了下面这个性能比较表,AFT-Full 可以在空间上比 Transformer 优化很多。改变的地方嘛就是那个 Multip-Head Attention。
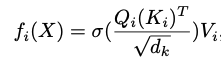
Attention的 MHA
把它重写成了下面这种格式:
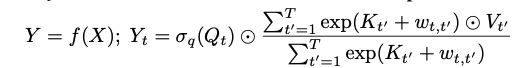
AttentionFree 的 MHA 替换
这样看来,实际上是把大量的矩阵运算替换成了点积运算。自然会把计算量降下来好多啊。
RWKV
RWKV 做为一个更新的表示形式,它会有什么操作呢?它分成了 Time-Mixing 与 Channel-Mixing 两个小模块。
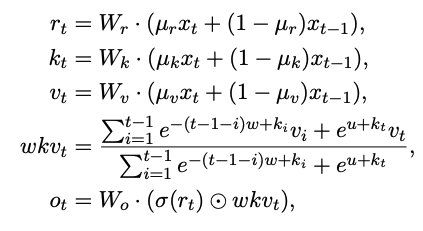
Time-Mixing
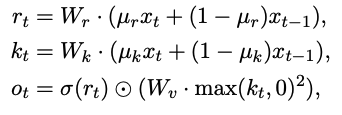
Channel-Mixing
这两个小模块又确实有基本的类似 RNN 的形式 Ot=f(Xt,Ot−1) ,现在这个形式是 Ot=f(Xt,Xt−1) 也就是有很明显的 RNN 的思在这个里边。虽然在我看依然是一个 Transformer 的优化变种,不是一个纯粹的 RNN 的形态。
看上面的公式,你就坐发现,它在 Inference 上要比 Transformer 的计算量小好多的。Training 这块每一个块的计算如果是 Transformer,那它所有的输入都是一次性计算的,尽管它计算量上有些大。对于 RWKV 来讲,这块应该是比较慢的,因为这个输入始终是串行的(如果我理解错了,再改,容我再去看看 http://proceedings.mlr.press/v119/katharopoulos20a/katharopoulos20a.pdf )。
https://github.com/BlinkDL/RWKV-LM 这个 GIT 项目里会有所有问题的答案。不过简单的来说吧。还是论文中的这一段:

都看到这儿了,我先给个建议吧:要不要考虑用魔法学习魔法。时代变革了,学习什么的,最重要的就是学 AI。工作什么的,最重要的就是用 AI。 而学习 AI,最好的方式应该是视频学习,类似 “知学堂推出的《程序员的AI大模型进阶之旅》”, 其实就是一份非常有意思的 AI 大模型的介绍性入门课程,简单看看,你可能马上就对大模型了解了,而不是要大量阅读。这也是个非常有效的学习方法。还有哦,加小助手的微信,好像有惊喜呢。
你要不要试一下
🔥2024大模型公开课👉训练方法+应用场景+个人增收
¥0.00点击领取
下面的就是 https://github.com/BlinkDL/ChatRWKV/blob/main/RWKV_in_150_lines.py 的代码,可以看到 RWKV 的核心代码还是相当简单的。这一段代码做推理,可以看到这个模型还是极简单的(我不太喜欢这种命名方式,就是)。
########################################################################################################
# The RWKV Language Model – https://github.com/BlinkDL/RWKV-LM
########################################################################################################
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(precision=4, suppress=True, linewidth=200)
import types, torch
from torch.nn import functional as F
from tokenizers import Tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer.from_file(“20B_tokenizer.json”)
args = types.SimpleNamespace()
args.MODEL_NAME = ‘/fsx/BlinkDL/HF-MODEL/rwkv-4-pile-430m/RWKV-4-Pile-430M-20220808-8066’
args.n_layer = 24
args.n_embd = 1024
context = “\nIn a shocking finding, scientist discovered a herd of dragons living in a remote, previously unexplored valley, in Tibet. Even more surprising to the researchers was the fact that the dragons spoke perfect Chinese.”
NUM_TRIALS = 3
LENGTH_PER_TRIAL = 100
TEMPERATURE = 1.0
TOP_P = 0.85
########################################################################################################
class RWKV_RNN(torch.jit.ScriptModule):
def __init__(self, args):
super().__init__()
self.args = args
self.eval() # set torch to inference mode
w = torch.load(args.MODEL_NAME + ‘.pth’, map_location=’cpu’)
for k in w.keys():
if ‘.time_’ in k: w[k] = w[k].squeeze()
if ‘.time_decay’ in k: w[k] = -torch.exp(w[k].float()) # the real time decay is like e^{-e^x}
else: w[k] = w[k].float() # convert to f32 type
self.w = types.SimpleNamespace() # set self.w from w
self.w.blocks = {}
for k in w.keys(): # example: “blocks.0.att.time_first” => self.w.blocks[0].att.time_first
parts = k.split(‘.’)
last = parts.pop()
here = self.w
for p in parts:
if p.isdigit():
p = int(p)
if p not in here: here[p] = types.SimpleNamespace()
here = here[p]
else:
if not hasattr(here, p): setattr(here, p, types.SimpleNamespace())
here = getattr(here, p)
setattr(here, last, w[k])
def layer_norm(self, x, w):
return F.layer_norm(x, (self.args.n_embd,), weight=w.weight, bias=w.bias)
@torch.jit.script_method
def channel_mixing(self, x, state, i:int, time_mix_k, time_mix_r, kw, vw, rw):
xk = x * time_mix_k + state[5*i+0] * (1 – time_mix_k)
xr = x * time_mix_r + state[5*i+0] * (1 – time_mix_r)
state[5*i+0] = x
r = torch.sigmoid(rw @ xr)
k = torch.square(torch.relu(kw @ xk)) # square relu, primer paper
return r * (vw @ k)
@torch.jit.script_method
def time_mixing(self, x, state, i:int, time_mix_k, time_mix_v, time_mix_r, time_first, time_decay, kw, vw, rw, ow):
xk = x * time_mix_k + state[5*i+1] * (1 – time_mix_k)
xv = x * time_mix_v + state[5*i+1] * (1 – time_mix_v)
xr = x * time_mix_r + state[5*i+1] * (1 – time_mix_r)
state[5*i+1] = x
r = torch.sigmoid(rw @ xr)
k = kw @ xk
v = vw @ xv
aa = state[5*i+2]
bb = state[5*i+3]
pp = state[5*i+4]
ww = time_first + k
qq = torch.maximum(pp, ww)
e1 = torch.exp(pp – qq)
e2 = torch.exp(ww – qq)
a = e1 * aa + e2 * v
b = e1 * bb + e2
wkv = a / b
ww = pp + time_decay
qq = torch.maximum(ww, k)
e1 = torch.exp(ww – qq)
e2 = torch.exp(k – qq)
state[5*i+2] = e1 * aa + e2 * v
state[5*i+3] = e1 * bb + e2
state[5*i+4] = qq
return ow @ (r * wkv)
def forward(self, token, state):
with torch.no_grad():
if state == None:
state = torch.zeros(self.args.n_layer * 5, self.args.n_embd)
for i in range(self.args.n_layer): state[5*i+4] = -1e30 # -infinity
x = self.w.emb.weight[token]
x = self.layer_norm(x, self.w.blocks[0].ln0)
for i in range(self.args.n_layer):
att = self.w.blocks[i].att
x = x + self.time_mixing(self.layer_norm(x, self.w.blocks[i].ln1), state, i,
att.time_mix_k, att.time_mix_v, att.time_mix_r, att.time_first, att.time_decay,
att.key.weight, att.value.weight, att.receptance.weight, att.output.weight)
ffn = self.w.blocks[i].ffn
x = x + self.channel_mixing(self.layer_norm(x, self.w.blocks[i].ln2), state, i,
ffn.time_mix_k, ffn.time_mix_r,
ffn.key.weight, ffn.value.weight, ffn.receptance.weight)
x = self.w.head.weight @ self.layer_norm(x, self.w.ln_out)
return x.float(), state
##########################################################################################################
def sample_logits(out, temperature=1.0, top_p=0.8):
probs = F.softmax(out, dim=-1).numpy()
sorted_probs = np.sort(probs)[::-1]
cumulative_probs = np.cumsum(sorted_probs)
cutoff = float(sorted_probs[np.argmax(cumulative_probs > top_p)])
probs[probs < cutoff] = 0
if temperature != 1.0:
probs = probs.pow(1.0 / temperature)
probs = probs / np.sum(probs)
out = np.random.choice(a=len(probs), p=probs)
return out
########################################################################################################
print(f’\nUsing CPU. Loading {args.MODEL_NAME} …’)
model = RWKV_RNN(args)
print(f’\nPreprocessing context (slow version. see v2/rwkv/model.py for fast version)’)
init_state = None
for token in tokenizer.encode(context).ids:
init_out, init_state = model.forward(token, init_state)
for TRIAL in range(NUM_TRIALS):
print(f’\n\n–[ Trial {TRIAL} ]—————–‘, context, end=””)
all_tokens = []
out_last = 0
out, state = init_out.clone(), init_state.clone()
for i in range(LENGTH_PER_TRIAL):
token = sample_logits(out, TEMPERATURE, TOP_P)
all_tokens += [token]
tmp = tokenizer.decode(all_tokens[out_last:])
if ‘\ufffd’ not in tmp: # only print when we have a valid utf-8 string
print(tmp, end=””, flush=True)
out_last = i + 1
out, state = model.forward(token, state)
print(‘\n’)
参考:
RWKV: Reinventing RNNs for the Transformer Era
https://github.com/BlinkDL/ChatRWKV/blob/main/RWKV_in_150_lines.py
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): A gentle Introduction and Overview










暂无评论内容