来自 Google Deepmind 开放权重的语言模型 Gemma 现已通过 Hugging Face 面向更广泛的开源社区开放。该模型提供了两个规模的版本:2B 和 7B 参数,包括预训练版本和经过指令调优的版本。它在 Hugging Face 平台上提供支持,可在 Vertex Model Garden 和 Google Kubernetes Engine 中轻松部署和微调。
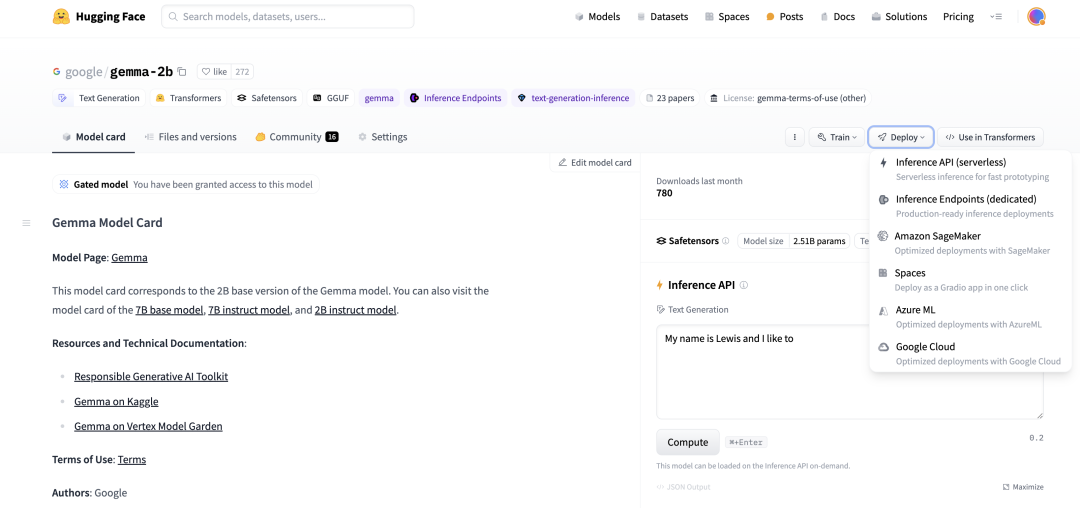
Gemma 模型系列同样非常适合利用 Colab 提供的免费 GPU 资源进行原型设计和实验。在这篇文章中,我们将简要介绍如何在 GPU 和 Cloud TPU 上,使用 Hugging Face Transformers 和 PEFT 库对 Gemma 模型进行参数高效微调(PEFT),这对想要在自己的数据集上微调 Gemma 模型的用户尤其有用。
为什么选择 PEFT?

即使对于中等大小的语言模型,常规的全参数训练也会非常占用内存和计算资源。对于依赖公共计算平台进行学习和实验的用户来说,如 Colab 或 Kaggle,成本可能过高。另一方面,对于企业用户来说,调整这些模型以适应不同领域的成本也是一个需要优化的重要指标。参数高效微调(PEFT)是一种以低成本实现这一目标的流行方法。
了解更多 PEFT 请参考文章:🤗 PEFT: 在低资源硬件上对十亿规模模型进行参数高效微调
在 GPU 和 TPU 上使用 PyTorch 进行 Gemma 模型的高效微调
在 Hugging Face 的 transformers 中,Gemma 模型已针对 PyTorch 和 PyTorch/XLA 进行了优化,使得无论是 TPU 还是 GPU 用户都可以根据需要轻松地访问和试验 Gemma 模型。随着 Gemma 的发布,我们还改善了 PyTorch/XLA 在 Hugging Face 上的 FSDP 使用体验。这种 FSDP 通过 SPMD 的集成还让其他 Hugging Face 模型能够通过 PyTorch/XLA 利用 TPU 加速。本文将重点介绍 Gemma 模型的 PEFT 微调,特别是低秩适应(LoRA)。
想要深入了解 LoRA 技术,我们推荐阅读 Lialin 等人的 “Scaling Down to Scale Up” 以及 Belkada 等人的 精彩文章。
使用低秩适应技术 (LoRA) 对大语言模型进行微调
低秩适应(LoRA)是一种用于大语言模型(LLM)的参数高效微调技术。它只针对模型参数的一小部分进行微调,通过冻结原始模型并只训练被分解为低秩矩阵的适配器层。PEFT 库 提供了一个简易的抽象,允许用户选择应用适配器权重的模型层。
from peft import LoraConfig
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=8,
target_modules=[“q_proj”, “o_proj”, “k_proj”, “v_proj”, “gate_proj”, “up_proj”, “down_proj”],
task_type=”CAUSAL_LM”,
)
在这个代码片段中,我们将所有的 nn.Linear 层视为要适应的目标层。
在以下示例中,我们将利用 QLoRA,出自 Dettmers 等人,通过 4 位精度量化基础模型,以实现更高的内存效率微调协议。通过首先在您的环境中安装 bitsandbytes 库,然后在加载模型时传递 BitsAndBytesConfig 对象,即可加载具有 QLoRA 的模型。
开始之前
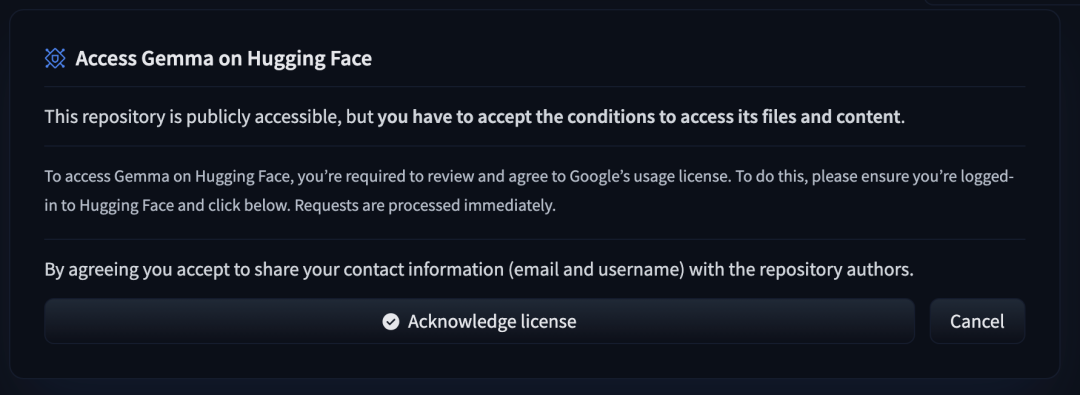
要访问 Gemma 模型文件,用户需先填写 同意表格。
我们继续。
微调 Gemma,让它学会并生成一些“名言金句”
假设您已提交同意表格,您可以从 Hugging Face Hub 获取模型文件。
地址:https://hf.co/collections/google/gemma-release-65d5efbccdbb8c4202ec078b
我们首先下载模型和分词器 (tokenizer),其中包含了一个 BitsAndBytesConfig 用于仅限权重的量化。
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
model_id = “google/gemma-2b”
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type=”nf4″,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, token=os.environ[‘HF_TOKEN’])
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=bnb_config, device_map={“”:0}, token=os.environ[‘HF_TOKEN’])
在开始微调前,我们先使用一个相当熟知的名言来测试一下 Gemma 模型:
text = “Quote: Imagination is more”
device = “cuda:0″
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors=”pt”).to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
模型完成了一个合理的补全,尽管有一些额外的 token:
Quote: Imagination is more important than knowledge. Knowledge is limited. Imagination encircles the world.
-Albert Einstein
I
但这并不完全是我们希望看到的答案格式。我们将尝试通过微调让模型学会以我们期望的格式来产生答案:
Quote: Imagination is more important than knowledge. Knowledge is limited. Imagination encircles the world.
Author: Albert Einstein
首先,我们选择一个英文“名人名言”数据集:
from datasets import load_dataset
data = load_dataset(“Abirate/english_quotes”)
data = data.map(lambda samples: tokenizer(samples[“quote”]), batched=True)
接下来,我们使用上述 LoRA 配置对模型进行微调:
import transformers
from trl import SFTTrainer
def formatting_func(example):
text = f”Quote: {example[‘quote’][0]}\nAuthor: {example[‘author’][0]}”
return [text]
trainer = SFTTrainer(
model=model,
train_dataset=data[“train”],
args=transformers.TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
warmup_steps=2,
max_steps=10,
learning_rate=2e-4,
fp16=True,
logging_steps=1,
output_dir=”outputs”,
optim=”paged_adamw_8bit”
),
peft_config=lora_config,
formatting_func=formatting_func,
)
trainer.train()
最终,我们再次使用先前的提示词,来测试模型:
text = “Quote: Imagination is”
device = “cuda:0″
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors=”pt”).to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=20)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
这次,我们得到了我们期待的答案格式:
Quote: Imagination is more important than knowledge. Knowledge is limited. Imagination encircles the world.
Author: Albert Einstein
名言:想象力比知识更重要,因为知识是有限的,而想象力概括着世界的一切.
作者:阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦
在 TPU 环境下微调,可通过 SPMD 上的 FSDP 加速
如前所述,Hugging Face transformers 现支持 PyTorch/XLA 的最新 FSDP 实现,这可以显著加快微调速度。只需在 transformers.Trainer 中添加 FSDP 配置即可启用此功能:
from transformers import DataCollatorForLanguageModeling, Trainer, TrainingArguments
# Set up the FSDP config. To enable FSDP via SPMD, set xla_fsdp_v2 to True.
fsdp_config = {
“fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap”: [“GemmaDecoderLayer”],
“xla”: True,
“xla_fsdp_v2”: True,
“xla_fsdp_grad_ckpt”: True
}
# Finally, set up the trainer and train the model.
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
train_dataset=data,
args=TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size=64, # This is actually the global batch size for SPMD.
num_train_epochs=100,
max_steps=-1,
output_dir=”./output”,
optim=”adafactor”,
logging_steps=1,
dataloader_drop_last = True, # Required for SPMD.
fsdp=”full_shard”,
fsdp_config=fsdp_config,
),
data_collator=DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(tokenizer, mlm=False),
)
trainer.train()
下一步
通过这个从源笔记本改编的简单示例,我们展示了应用于 Gemma 模型的 LoRA 微调方法。完整的 GPU colab 在 这里 可以找到,完整的 TPU 脚本在 这里可以找到。我们对于这一最新加入我们开源生态系统的成员所带来的无限研究和学习机会感到兴奋。我们鼓励用户也浏览 Gemma 文档 和我们的 发布博客,以获取更多关于训练、微调和部署 Gemma 模型的示例。
查看文内链接,请点击阅读原文在 Hugging Face 博客上查看:
https://hf.co/blog/zh/gemma-peft









暂无评论内容